
H(οT) = The amount of dirt removed does not depend on the temperature. H(οD) = The amount of dirt removed does not depend on the type of detergent. In this example, we are interested in testing Null Hypothesis. Then you divide your laundry randomly into “6*r” pile of equal size and assign each ‘r’ piles into the combination of (“super” and “Best”) and (“cold”, “warm” and “hot”). To this end you buy two detergents with different brand (“Super” and “Best”) and choose three different temperature levels (“cold”, “warm” and “hot”). We will do two way ANOVA with example, lets start the calculationĮxample: Suppose you want to determine whether the brand of laundry detergent used and the temperature affects the amount of dirt removed from your laundry. Assumption #6: There needs to be homogeneity of variances for each combination of the groups of the two independent variables.Assumption #5: Your dependent variable should be approximately normally distributed for each combination of the groups of the two independent variables.Outliers are data points within your data that do not follow the usual pattern Assumption #4: There should be no significant outliers.Assumption #3: You should have independence of observations, which means that there is no relationship between the observations in each group or between the groups themselves.
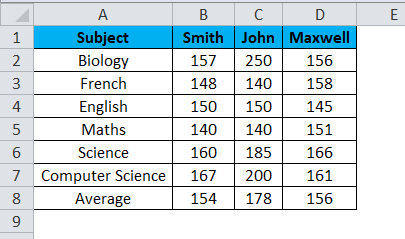
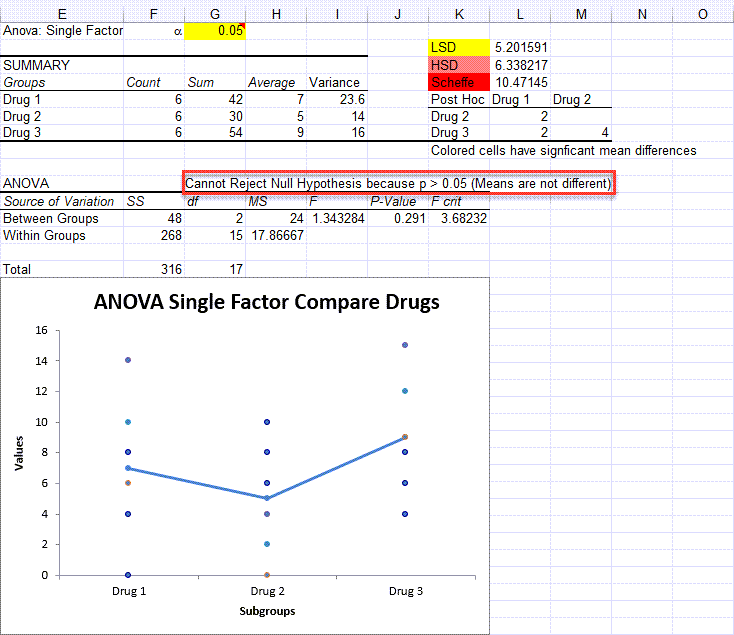
For example, you may want to determine whether there is an interaction between physical activity level(IV) and gender(IV) on blood cholesterol concentration(DV) in children.
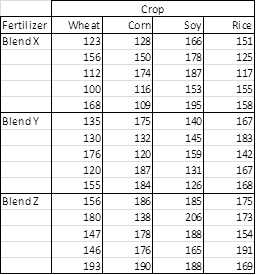
The primary purpose of a two-way ANOVA… is to understand if there is an interaction between the two independent variables on the dependent variable. The two-way ANOVA compares the mean differences between groups that have been split on two independent variables (called factors).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
